Connect A New Online Channel¶
The tutorial will walk you through the process of adding support for a new online channel - in this case, LinkedIn - to CampaignChain by creating and programming the necessary modules and packaging them into a Symfony bundle.
The new LinkedIn bundle will include functionality to connect to a user’s LinkedIn activity stream and post updates to it.
Assumptions and Prerequisites¶
- You have a Symfony environment meeting all the system requirements.
- You have a working CampaignChain development installation.
- You have a good understanding of the OAuth authentication process.
- You have a reasonable understanding of the LinkedIn REST API. Learn more about the API.
- You have an application registered with LinkedIn and have obtained the necessary keys. Register your application.
Overview¶
To connect a new online channel through CampaignChain, here are the steps you will follow:
- Generate Channel and Location bundles
- Define configuration files for the Channel and Location bundles
- Define routes for your Channel and Location modules
- Create Channel and Location controllers and views
- Add a channel icon
To enable activities and operations for the new channel, here are the steps you will follow:
- Generate Activity and Operation bundles
- Define configuration files for the Activity and Operation bundles
- Understand the API exposed by the channel you’re connecting
- Create entities and entity managers for your Activities and Operations
- Create input forms and connect them to your entities
- Create an API client and job processor
- Define routes for your Activity and Operation modules
- Create an Activity controller
Connect Channels and Locations¶
1. Generate Channel and Location bundles¶
The first step is to create a bundle for the LinkedIn channel. In this case, we’ll assume the organization name is Acme, and use this organization name for the module namespaces.
The following commands walk you through the process. Note that you’re safe using Symfony’s defaults for all interactive prompts except for certain items shown below
$ php app/console generate:bundle
Bundle namespace: Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle
Configuration format (yml, xml, php, or annotation): yml
Do you want to generate the whole directory structure [no]? yes
Symfony will now produce a new bundle containing stub code and files, in the location your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle. The name of the bundle will be AcmeCampaignChainChannelLinkedInBundle.
Follow the steps above to generate a similar bundle for a location in the channel. In this tutorial, the location will be the user’s LinkedIn activity stream. When creating this bundle, you will specify the bundle namespace as Acme/CampaignChain/Location/LinkedInBundle. The new bundle will be created at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle with the name AcmeCampaignChainLocationLinkedInBundle.
2. Create Configuration Files¶
Every CampaignChain bundle needs two configuration files: composer.json and campaignchain.yml. So the next step is to create these configuration files for your Channel and Location bundles.
To begin, create the composer.json file for the Channel bundle:
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/composer.json
{
"name": "acme/channel-linkedin",
"description": "Connect with LinkedIn",
"keywords": ["linkedin","oauth"],
"type": "campaignchain-channel",
"homepage": "http://example.ac.me",
"license": "Proprietary",
"authors": [
{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.ac.me"
}
],
"require": {
"campaignchain/core": "dev-master",
"campaignchain/security-authentication-client-oauth": "dev-master"
}
}
The important point to note here is the type parameter, which specifies the bundle type as ‘campaignchain-channel’.
You should also create a composer.json for the Location bundle, as shown below:
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Location/LinkedInBundle/composer.json
{
"name": "acme/location-linkedin",
"description": "LinkedIn user stream.",
"keywords": ["linkedin", "user", "stream"],
"type": "campaignchain-location",
"homepage": "http://example.ac.me",
"license": "Proprietary",
"authors": [
{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.ac.me"
}
],
"require": {
"acme/channel-linkedin": "dev-master"
}
}
Notice again that the type parameter reflects the new bundle type - in this case, ‘campaignchain-location’ - and the require parameter specifies a dependency on the previous Channel bundle, by using the name defined in the Channel bundle’s composer.json file.
In addition to composer.json, every CampaignChain bundle must also include an campaignchain.yml file, which CampaignChain uses to correctly wire the module(s) in the bundle into the system.
Note
Although an CampaignChain bundle can contain multiple modules, we’ll keep things simple in this tutorial and assume that each bundle contains only a single module.
Your next step is to define the Channel bundle’s campaignchain.yml file, which specifies the display name for the LinkedIn Channel module, any routes used by the module and any hooks. Here’s what the file looks like:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/campaignchain.yml
modules:
acme-linkedin:
display_name: LinkedIn
routes:
new: acme_campaignchain_channel_linkedin_create
hooks:
campaignchain-assignee: true
Following CampaignChain conventions, the Channel module name includes the vendor name and a string that describes the purpose of the module - in this case, ‘acme-linkedin’. The module configuration also specifies the name of the Symfony route to be used when creating a new channel (you’ll define this route and its associated view script in the next few steps) and any hooks used by the module.
Once the Channel module is defined, the next step is to tell CampaignChain about the locations supported by the channel. This is specified via the Location bundle’s campaignchain.yml file, as shown below:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Location/LinkedInBundle/campaignchain.yml
modules:
acme-linkedin-user:
display_name: LinkedIn user stream
This configuration informs CampaignChain about the location module representing the LinkedIn user stream and specifies its display name in the CampaignChain GUI. Note that as before, the Location module name contains the vendor name and a brief descriptive string identifying the location.
3. Define Channel Routes¶
In general, a Channel module should take care of creating a new location and handling authentication between CampaignChain and the channel. This implies that the Channel module should define two routes: one to create a new channel (‘new’) and one to handle authentication (‘login’).
In the previous step, you specified the name for the Channel module’s ‘new’ route. Now, it’s time to follow through by actually defining the URLs for the ‘new’ route and the additional required ‘login’ route, and their respective controller actions.
To do this, update the file your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml as shown below:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml
acme_campaignchain_channel_linkedin_create:
pattern: /channel/linkedin/create
defaults: { _controller: AcmeCampaignChainChannelLinkedInBundle:LinkedIn:create }
acme_campaignchain_channel_linkedin_login:
pattern: /channel/linkedin/create/login
defaults: { _controller: AcmeCampaignChainChannelLinkedInBundle:LinkedIn:login }
Note
You can delete the default ‘hello’ route added by the Symfony bundle generator in the above file. Similarly, you can delete the default ‘hello’ route in the Location module’s routing.xml file, which can be found at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Location/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml.
4. Add Controllers and Views¶
Next, you’ll need to create views and controllers for the routes above. First up, you’ll handle the ‘new’ route, by creating a LinkedInController with a createAction() method, as shown below.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Controller/LinkedInController.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Channel\LinkedInBundle\Controller;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location;
use Acme\CampaignChain\Location\LinkedInBundle\Entity\LinkedInUser;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Session\Session;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
class LinkedInController extends Controller
{
const RESOURCE_OWNER = 'LinkedIn';
private $applicationInfo = array(
'key_labels' => array('key', 'App Key'),
'secret_labels' => array('secret', 'App Secret'),
'config_url' => 'https://www.linkedin.com/secure/developer',
'parameters' => array(
"force_login" => true,
),
);
public function createAction()
{
$oauthApp = $this->get(
'campaignchain.security.authentication.client.oauth.application'
);
$application = $oauthApp->getApplication(self::RESOURCE_OWNER);
if(!$application){
return $oauthApp->newApplicationTpl(self::RESOURCE_OWNER,
$this->applicationInfo);
}
else {
return $this->render(
'AcmeCampaignChainChannelLinkedInBundle:Create:index.html.twig',
array(
'page_title' => 'Connect with LinkedIn',
'app_id' => $application->getKey(),
)
);
}
}
}
The createAction() method wraps CampaignChain’s OAuth module and renders a splash page asking the user to connect to the LinkedIn account by providing credentials and granting permission to CampaignChain to access user data. This page is rendered with the view script shown below:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Resources/views/Create/index.html.twig
{% extends 'CampaignChainCoreBundle:Base:base.html.twig' %}
{% block body %}
<div class="jumbotron">
<p>Connect to the LinkedIn account by logging in to LinkedIn. Your username
and password will remain with LinkedIn and will not be stored in this
application.</p>
<p><a class="btn btn-primary btn-lg" role="button"
onclick="popupwindow('{{ path('acme_campaignchain_channel_linkedin_login') }}',
'',600,600);">Connect now</a></p>
</div>
{% endblock %}
Clicking the “Connect now” button in the above view activates the ‘login’ route defined earlier. You now need to write a corresponding controller action to use the credentials entered by the user, attempt authentication and if successful, add the location to the CampaignChain database for later use.
To simplify this task, CampaignChain provides a Location service and a Channel Wizard which together encapsulate most of the functionality you will need. The code below illustrates the typical process:
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Controller/LinkedInController.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Channel\LinkedInBundle\Controller;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location;
use Acme\CampaignChain\Location\LinkedInBundle\Entity\LinkedInUser;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Session\Session;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
class LinkedInController extends Controller
{
public function loginAction(Request $request){
$oauth =
$this->get(
'campaignchain.security.authentication.client.oauth.authentication'
);
$status = $oauth->authenticate(self::RESOURCE_OWNER,
$this->applicationInfo);
$profile = $oauth->getProfile();
if($status){
try {
$repository = $this->getDoctrine()->getManager();
$repository->getConnection()->beginTransaction();
$wizard = $this->get('campaignchain.core.channel.wizard');
$wizard->setName($profile->displayName);
// Get the location module.
$locationService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.location');
$locationModule = $locationService->getLocationModule(
'acme/location-linkedin', 'acme-linkedin-user');
$location = new Location();
$location->setIdentifier($profile->identifier);
$location->setName($profile->displayName);
$location->setLocationModule($locationModule);
$location->setImage($profile->photoURL);
$location->setURL($profile->profileURL);
$wizard->addLocation($location->getIdentifier(), $location);
$channel = $wizard->persist();
$wizard->end();
$oauth->setLocation($channel->getLocations()[0]);
$linkedinUser = new LinkedInUser();
$linkedinUser->setLocation($channel->getLocations()[0]);
$linkedinUser->setIdentifier($profile->identifier);
$linkedinUser->setDisplayName($profile->displayName);
$linkedinUser->setProfileImageURL($profile->photoURL);
$linkedinUser->setProfileURL($profile->profileURL);
$repository->persist($linkedinUser);
$repository->flush();
$repository->getConnection()->commit();
$this->get('session')->getFlashBag()->add(
'success',
'The LinkedIn location <a href="#">'.
$profile->displayName.'</a> was connected
successfully.'
);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$repository->getConnection()->rollback();
throw $e;
}
} else {
// A channel already exists that has been connected
// with this Facebook account
$this->get('session')->getFlashBag()->add(
'warning',
'A location has already been connected for this LinkedIn account.'
);
}
return $this->render(
'AcmeCampaignChainChannelLinkedInBundle:Create:login.html.twig',
array(
'redirect' => $this->generateUrl('campaignchain_core_channel')
)
);
}
}
The first few lines of the loginAction() action method use CampaignChain’s OAuth module to authenticate against the remote service. If authentication is successful, the OAuth object’s getProfile() method returns the profile of the authenticated user. This location now needs to be added to CampaignChain’s database.
To accomplish this, the action method first creates a new Channel Wizard object, which is a convenience object that makes it easy to connect the new location to the channel and save it to CampaignChain’s database. The Channel Wizard is invoked as a Symfony service. The Channel Wizard is also assigned a name using its setName() method; this could be a fixed name, or based on input entered by the user (although you’d need to provide a form field in the view to accept this input).
Every channel must have at least one location. The action method then calls CampaignChain’s Location service to identify the Location module. The Location bundle’s name and unique module identifier play a critical role in helping the Channel Wizard correctly identify and store the location so that CampaignChain can correctly generate routes for the location.
The method initializes a new Location object using the information from the returned user profile, and attaches this Location object to the channel using the channel wizard’s addLocation() method. The information about the new location is saved to the database using the channel wizard’s persist() method.
Since every location is typically associated with a user, it makes sense to also store information about the user in the CampaignChain database. The typical properties you’d want to store are the user identifier, first name, last name, email address, profile URL and profile image URL, plus any properties specific to the channel you’re connecting.
The action method above uses a LinkedInUser object, implemented as a Doctrine entity with properties for the user identifier, first name, last name, email address, LinkedIn profile URL and LinkedIn profile image URL. The code for this LinkedInUser entity is as follows:
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Location/LinkedInBundle/Entity/LinkedInUser.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Location\LinkedInBundle\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
/**
* @ORM\Entity
* @ORM\Table(name="acme_location_linkedin_user")
*/
class LinkedInUser
{
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="integer")
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="AUTO")
*/
protected $id;
/**
* @ORM\OneToOne(targetEntity="CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location",
* cascade={"persist"})
*/
protected $location;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, unique=true)
*/
protected $identifier;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, name="display_name")
*/
protected $displayName;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, name="first_name", nullable=true)
*/
protected $firstName;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, name="last_name", nullable=true)
*/
protected $lastName;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, nullable=true)
*/
protected $email;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, name="profile_url", nullable=true)
*/
protected $profileURL;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, name="profile_image_url",
* nullable=true)
*/
protected $profileImageURL;
/**
* Get id
*
* @return integer
*/
public function getId()
{
return $this->id;
}
/**
* Set identifier
*
* @param string $identifier
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setIdentifier($identifier)
{
$this->identifier = $identifier;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get identifier
*
* @return string
*/
public function getIdentifier()
{
return $this->identifier;
}
/**
* Set displayName
*
* @param string $displayName
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setDisplayName($displayName)
{
$this->displayName = $displayName;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get displayName
*
* @return string
*/
public function getDisplayName()
{
return $this->displayName;
}
/**
* Set firstName
*
* @param string $firstName
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setFirstName($firstName)
{
$this->firstName = $firstName;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get firstName
*
* @return string
*/
public function getFirstName()
{
return $this->firstName;
}
/**
* Set lastName
*
* @param string $lastName
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setLastName($lastName)
{
$this->lastName = $lastName;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get lastName
*
* @return string
*/
public function getLastName()
{
return $this->lastName;
}
/**
* Set email
*
* @param string $email
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setEmail($email)
{
$this->email = $email;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get email
*
* @return string
*/
public function getEmail()
{
return $this->email;
}
/**
* Set profileURL
*
* @param string $profileURL
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setProfileURL($profileURL)
{
$this->profileURL = $profileURL;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get profileURL
*
* @return string
*/
public function getProfileURL()
{
return $this->profileURL;
}
/**
* Set profileImageURL
*
* @param string $profileImageURL
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setProfileImageURL($profileImageURL)
{
$this->profileImageURL = $profileImageURL;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get profileImageURL
*
* @return string
*/
public function getProfileImageURL()
{
return $this->profileImageURL;
}
/**
* Set location
*
* @param \CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location $location
* @return LinkedInUser
*/
public function setLocation(\CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location
$location = null)
{
$this->location = $location;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get location
*
* @return \CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location
*/
public function getLocation()
{
return $this->location;
}
/**
* Constructor
*/
public function __construct()
{
}
}
5. Add a Channel Icon¶
Every Channel module should include a channel icon image, for easy identification within the CampaignChain GUI. In most cases, the channel you’re trying to connect to will provide a logo image, so all that’s really needed is to resize it to 16x16 pixels and save it in PNG format.
Note
Remember to read the channel’s terms of use for its images, ensure that your usage of the image is compliant and provide an image credit, link and/or attribution as needed.
For the LinkedIn Channel module created in this tutorial, the channel icon image should be saved to your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Location/LinkedInBundle/Resources/public/images/icons/16x16/linkedin.png. The name of the image (‘linkedin’) should match the descriptive string used in the bundle name (‘acme/channel-linkedin’)
At this point, your Channel and Location bundles are complete.
Define Activities and Operations¶
With the Channel and Location defined, the next step is to define the Activities and Operations possible. To keep things simple, we’ll assume that only a single Activity is required: sharing news on the user’s LinkedIn stream. This will be accomplished using LinkedIn’s Share API, which makes it possible to add posts to a user’s LinkedIn social stream using REST.
1. Generate Activity and Operation bundles¶
The first step here is again to create bundles for the Activity and Operation. Remember that every Activity must have at least one Operation. In this case, since only one Operation is needed, the Activity is equal to the Operation (and you’ll see further along how to let CampaignChain know this).
The command to create a new bundle is explained earlier. Here it is again:
$ php app/console generate:bundle
When creating the Activity bundle, you will specify the bundle namespace as Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle. The new bundle will be created at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle with the name AcmeCampaignChainActivityLinkedInBundle.
When creating the Operation bundle, you will specify the bundle namespace as Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle. The new bundle will be created at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle with the name AcmeCampaignChainOperationLinkedInBundle.
2. Create Configuration Files¶
The next step is to create configuration files for your Activity and Operation bundles.
To begin, create the composer.json file for the Activity bundle:
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/composer.json
{
"name": "acme/activity-linkedin",
"description": "Post a news update on a LinkedIn stream.",
"keywords": ["linkedin","news"],
"type": "campaignchain-activity",
"homepage": "http://example.ac.me",
"license": "Proprietary",
"authors": [
{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.ac.me"
}
],
"require": {
"campaignchain/core": "dev-master",
"campaignchain/location-linkedin": "dev-master",
"campaignchain/operation-linkedin": "dev-master",
"campaignchain/hook-due": "dev-master"
}
}
You will notice that the type parameter specifies the bundle type as ‘campaignchain-activity’. Notice also that the require parameter includes dependencies for the corresponding Operation bundle, as well as CampaignChain’s due hook. The latter is needed so that activities and operations can be scheduled for automatic execution at specific times in the future.
You should also create a composer.json for the Operation bundle, as shown below:
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/composer.json
{
"name": "acme/operation-linkedin",
"description": "Collection of various LinkedIn operations.",
"keywords": ["linkedin","operation"],
"type": "campaignchain-operation",
"homepage": "http://example.ac.me",
"license": "Proprietary",
"authors": [
{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.ac.me"
}
]
}
By now, it should be clear that the type parameter for Operation bundles must hold the value ‘campaignchain-operation’...and that’s clearly seen in the above definition as well.
Your next step is to define the Activity bundle’s campaignchain.yml file, which specifies the display name for the LinkedIn Activity module, any routes used by the module and any hooks. Here’s what the file looks like:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/campaignchain.yml
modules:
acme-linkedin-share-news-item:
display_name: 'Share News'
channels:
- acme/channel-linkedin/acme-linkedin
routes:
new: acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_new
edit: acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_edit
edit_modal: acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_edit_modal
edit_api: acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_edit_api
hooks:
campaignchain-due: true
Following CampaignChain conventions, the Activity module name includes the vendor name and a string that describes the purpose of the module - in this case, ‘acme-linkedin-share-news-item’. The module configuration also specifies the display name to be used in the CampaignChain GUI, the names of the Symfony route to be used when creating or editing activities, and any hooks used by the module.
An important addition in the Activity bundle’s campaignchain.yml file is the channels parameter, which specifies the link between the channel and the activity. The format of the value is the Channel bundle name, followed by the Channel module name, separated by slashes. In this case, the value ‘acme/channel-linkedin/acme-linkedin’ points to the Channel bundle created earlier (‘acme/channel-linkedin’) and the Channel module within it (‘acme-linkedin’).
Once the Activity module is defined, the next step is to tell CampaignChain about the operations supported by the activity. This is specified via the Operation bundle’s campaignchain.yml file, as shown below:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/campaignchain.yml
modules:
acme-linkedin-share-news-item:
display_name: 'Share News'
owns_location: true
services:
job: acme.operation.linkedin.job.share_news_item
This configuration informs CampaignChain about the Operation module representing the news sharing operation for LinkedIn. As before, the Operation module name contains the vendor name and a brief descriptive string identifying the operation.
Since the Operation module will also create a new Location (in this case, a new post in the LinkedIn stream which is accessible directly via a unique URL), it’s important to tell CampaignChain that the Operation will own the new Location, via the owns_location parameter.
Finally, since the Operation needs to expose a Job (which will be run by CampaignChain’s global scheduler and which we’ll define further along), the configuration specifies the name for this job service so CampaignChain can easily invoke it.
4. Create An Entity and Entity Manager¶
In this step, you will create an entity to represent a LinkedIn news item. The code for this NewsItem entity is as follows and it should be saved to your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Entity/NewsItem.php.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Entity/NewsItem.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
/**
* @ORM\Entity
* @ORM\Table(name="acme_operation_linkedin_news_item")
*/
class NewsItem
{
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="integer")
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="AUTO")
*/
protected $id;
/**
* @ORM\OneToOne(targetEntity="CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Operation",
* cascade={"persist"})
*/
protected $operation;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="text")
*/
protected $message;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="text")
*/
protected $linkTitle;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="text")
*/
protected $linkDescription;
/**
* URL included within the share content
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, name="linkUrl", nullable=true)
*/
protected $linkUrl;
/**
* direct URL to the share
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=255, nullable=true)
*/
protected $url;
/**
* Get id
*
* @return integer
*/
public function getId()
{
return $this->id;
}
/**
* Set message
*
* @param string $message
* @return Status
*/
public function setMessage($message)
{
$this->message = $message;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get message
*
* @return string
*/
public function getMessage()
{
return $this->message;
}
/**
* Set title
*
* @param string $linkTitle
* @return Status
*/
public function setLinkTitle($linkTitle)
{
$this->linkTitle = $linkTitle;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get title
*
* @return string
*/
public function getLinkTitle()
{
return $this->linkTitle;
}
/**
* Set description
*
* @param string $linkDescription
* @return Status
*/
public function setLinkDescription($linkDescription)
{
$this->linkDescription = $linkDescription;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get description
*
* @return string
*/
public function getLinkDescription()
{
return $this->linkDescription;
}
/**
* Set submit URL
*
* @param string $linkUrl
* @return Status
*/
public function setLinkUrl($linkUrl)
{
$this->linkUrl = $linkUrl;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get submit URL
*
* @return string
*/
public function getLinkUrl()
{
return $this->linkUrl;
}
/**
* Set url
*
* @param string $url
* @return Status
*/
public function setUrl($url)
{
$this->url = $url;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get url
*
* @return string
*/
public function getUrl()
{
return $this->url;
}
/**
* Set operation
*
* @param \CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Operation $operation
* @return Status
*/
public function setOperation(\CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Operation
$operation = null)
{
$this->operation = $operation;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get operation
*
* @return \CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Operation
*/
public function getOperation()
{
return $this->operation;
}
}
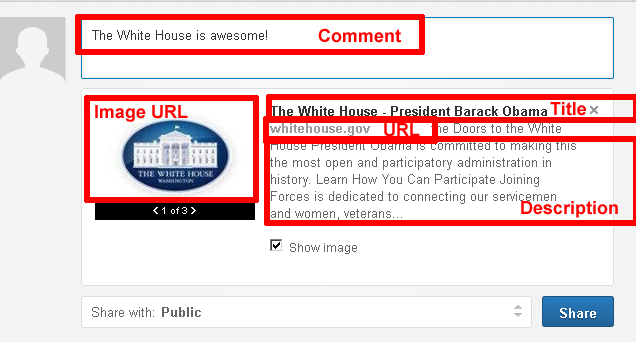
As you can see, the entity includes proeprties corresponding to those expected by the LinkedIn Share API (the image URL field is omitted for simplicity), as well as some properties needed by CampaignChain.
You will also need an entity service manager, which will retrieve an instance of the entity by its identifier. Here’s the code, which should be saved to your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/EntityService/NewsItem.php.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/EntityService/NewsItem.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\EntityService;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManager;
class NewsItem
{
protected $em;
public function __construct(EntityManager $em)
{
$this->em = $em;
}
public function getNewsItemByOperation($id){
$newsitem = $this->em
->getRepository('AcmeCampaignChainOperationLinkedInBundle:NewsItem')
->findOneByOperation($id);
if (!$newsitem) {
throw new \Exception(
'No news item found by operation id '.$id
);
}
return $newsitem;
}
}
The getNewsItemByOperation() method takes care of retrieving a specific news item using its unique identifier in the database.
This is also a good point to update the Operation module’s list of exposed services to include the new entity service manager. To do this, update the file at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/services.yml with the following information.
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/services.yml
parameters:
services:
acme.operation.linkedin.news_item:
class: Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\EntityService\NewsItem
arguments: [ @doctrine.orm.entity_manager ]
5. Create an Input Form for Entity Data¶
With the entity created, the next step is to provide an input form that will be rendered by the CampaignChain user interface. This form will be used when setting up a new LinkedIn news item, and the fields in the form must therefore correspond with the properties of the NewsItem entity.
The easiest way to create the form is by using Symfony’s Form component and FormBuilder interface. The following code, which should be saved to your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Form/Type/ShareNewsItemOperationType.php, illustrates how to do this.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Form/Type/ShareNewsItemOperationType.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Form\Type;
use Symfony\Component\Form\AbstractType;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormBuilderInterface;
use Symfony\Component\OptionsResolver\OptionsResolverInterface;
use Symfony\Component\DependencyInjection\ContainerInterface;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManager;
class ShareNewsItemOperationType extends AbstractType
{
private $newsitem;
private $view = 'default';
protected $em;
protected $container;
public function __construct(EntityManager $em, ContainerInterface $container)
{
$this->em = $em;
$this->container = $container;
}
public function setNewsItem($newsitem){
$this->newsitem = $newsitem;
}
public function setView($view){
$this->view = $view;
}
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('message', 'text', array(
'property_path' => 'message',
'label' => 'Message',
'attr' => array(
'placeholder' => 'Add message...',
'max_length' => 200
)
));
$builder
->add('linkTitle', 'text', array(
'property_path' => 'linkTitle',
'label' => 'Title of page being shared',
'attr' => array(
'placeholder' => 'Add title...',
'max_length' => 140
)
));
$builder
->add('description', 'textarea', array(
'property_path' => 'linkDescription',
'label' => 'Description of page being shared',
'attr' => array(
'placeholder' => 'Add description...',
'max_length' => 300
)
));
$builder
->add('submitUrl', 'text', array(
'property_path' => 'linkUrl',
'label' => 'URL of page being shared',
'attr' => array(
'placeholder' => 'Add URL...',
'max_length' => 255
)
));
}
public function setDefaultOptions(OptionsResolverInterface $resolver)
{
$defaults = array(
'data_class' =>
'CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Entity\NewsItem',
);
if($this->newsitem){
$defaults['data'] = $this->newsitem;
}
$resolver->setDefaults($defaults);
}
public function getName()
{
return 'acme_operation_linkedin_share_news_item';
}
}
The main work here is done by the buildForm() method, which takes care of creating the necessary form fields, and the setDefaultOptions() method, which links the data entered into the form with the NewsItem entity created earlier.
6. Create an API Client and Job Processor¶
In the previous steps, you enabled the user to enter details of a new LinkedIn news item into a form and have that data saved to the CampaignChain database. The next step is to massage that data into the format needed by the LinkedIn API and then transfer it to the API in an authenticated request.
To accomplish this task, it is necessary to create an HTTP client object which will ease communication with the LinkedIn API. CampaignChain already comes with an OAuth client, which you used previously in your LinkedIn Channel module. You can use this client’s built-in functionality to take care of most of the authentication tasks.
To do this, go back to your Channel module and add the following LinkedInClient object to it, at the location your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/REST/LinkedInClient.php.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/REST/LinkedInClient.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Channel\LinkedInBundle\REST;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Session\Session;
use Guzzle\Http\Client;
use Guzzle\Plugin\Oauth\OauthPlugin;
class LinkedInClient
{
const RESOURCE_OWNER = 'LinkedIn';
const BASE_URL = 'https://api.linkedin.com/v1';
protected $container;
public function setContainer($container)
{
$this->container = $container;
}
public function connectByActivity($activity){
$oauthApp = $this->container->get(
'campaignchain.security.authentication.client.oauth.application'
);
$application = $oauthApp->getApplication(self::RESOURCE_OWNER);
$oauthToken = $this->container->get(
'campaignchain.security.authentication.client.oauth.token'
);
$token = $oauthToken->getToken($activity->getLocation());
return $this->connect(
$application->getKey(),
$application->getSecret(),
$token->getAccessToken(),
$token->getTokenSecret()
);
}
public function connect($appKey, $appSecret, $accessToken, $tokenSecret) {
try {
$client = new Client(self::BASE_URL.'/');
$oauth = new OauthPlugin(array(
'consumer_key' => $appKey,
'consumer_secret' => $appSecret,
'token' => $accessToken,
'token_secret' => $tokenSecret,
));
return $client->addSubscriber($oauth);
}
catch (ClientErrorResponseException $e) {
$request = $e->getRequest();
$response = $e->getResponse();
print_r($response);
}
catch (ServerErrorResponseException $e) {
$request = $e->getRequest();
$response = $e->getResponse();
print_r($response);
}
catch (BadResponseException $e) {
$request = $e->getRequest();
$response = $e->getResponse();
print_r($response);
}
catch(Exception $e){
print_r($e->getMessage());
}
}
}
The two important values set in this client are the constants at the top: the RESOURCE_OWNER constant specifies the owning channel, which is then used to retrieve the keys and secrets needed for an authenticated API connection, and the BASE_URL constant specifies the base URL for all API requests.
You will also need to update the Channel module’s list of exposed services to include the new client. To do this, update the file at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/services.yml with the following information.
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Channel/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/services.yml
parameters:
services:
acme.channel.linkedin.rest.client:
class: Acme\CampaignChain\Channel\LinkedInBundle\REST\LinkedInClient
calls:
- [setContainer, ["@service_container"]]
You’ll notice that this client object merely takes care of connecting and authenticating against the LinkedIn API. It doesn’t actually take care of creating and sending a POST request to the Share API. That task is handled by a separate Job object, which should be created within your Operation module at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Job/ShareNewsItem.php.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Job/ShareNewsItem.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Job;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Action;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManager;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Medium;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Job\JobServiceInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
class ShareNewsItem implements JobServiceInterface
{
protected $em;
protected $container;
protected $message;
protected $linkTitle;
protected $linkDescription;
protected $linkUrl;
public function __construct(EntityManager $em, $container)
{
$this->em = $em;
$this->container = $container;
}
public function execute($operationId)
{
$newsitem = $this->em
->getRepository('AcmeCampaignChainOperationLinkedInBundle:NewsItem')
->findOneByOperation($operationId);
if (!$newsitem) {
throw new \Exception(
'No news item found for an operation with ID: '.$operationId
);
}
// Process the link URL to append the Tracking ID attached for
// call to action tracking.
$ctaService = $this->container->get('campaignchain.core.cta');
$newsitem->setLinkUrl(
$ctaService->processCTAs(
$newsitem->getLinkUrl(),
$newsitem->getOperation()
)
->getContent()
);
$client = $this->container->get('acme.channel.linkedin.rest.client');
$connection = $client->connectByActivity(
$newsitem->getOperation()->getActivity()
);
$xmlBody = "<share><comment>" . $newsitem->getMessage() .
"</comment><content><title>" . $newsitem->getLinkTitle() .
"</title><description>" . $newsitem->getLinkDescription() .
"</description><submitted-url>" . $newsitem->getLinkUrl() .
"</submitted-url></content><visibility><code>anyone</code></visibility></share>";
$request = $connection->post(
'people/~/shares',
array('headers' => array('Content-Type' => 'application/xml')),
$xmlBody
);
$response = $request->send()->xml();
$newsitemUrl = (string)$response->{'update-url'};
$newsitemId = (string)$response->{'update-key'};
$newsitem->setUrl($newsitemUrl);
// Set Operation to closed.
$newsitem->getOperation()->setStatus(Action::STATUS_CLOSED);
$location = $newsitem->getOperation()->getLocations()[0];
$location->setIdentifier($newsitemId);
$location->setURL($newsitemUrl);
$location->setName($status->getOperation()->getName());
$location->setStatus(Medium::STATUS_ACTIVE);
$this->em->flush();
$this->message = 'The message "'.$newsitem->getMessage().'" with the ID "'.
$newsitemId.'" has been posted on LinkedIn. See it on LinkedIn:
<a href="'.$newsitemUrl.'">'.$newsitemUrl.'</a>';
return self::STATUS_OK;
}
public function getMessage(){
return $this->message;
}
}
A Job object is always part of an Operation module and it is called as necessary to perform the corresponding operation. It should implement the JobServiceInterface, which mandates an execute() method which is called when the job is executed.
If you look into the execute() method above, you’ll see that it begins by retrieving the required news item from the CampaignChain database (using the news item’s identifier). Then it passes the link URL to CampaignChain’s CTA service so that CampaignChain can store the URL as a Call to Action and track it. It also invokes the LinkedIn client created earlier as a Symfony service and uses the client to authenticate against the LinkedIn API.
The next step is to generate an XML document containing the details of the news item to be posted, in the format expected by the LinkedIn API. This XML document is then transmitted to the API endpoint https://api.linkedin.com/v1/people/~/shares in a POST request using the client’s inherited post() method. The XML response is converted to a SimpleXML object for easy processing.
The XML response contains two useful pieces of information: the LinkedIn identifier for the news item, and the direct URL to it. The remainder of the execute() method is concerned with saving this information to the CampaignChain database, updating the status of the operation and presenting a success message to the user.
Given that the shared news has a dedicated URL on Linkedin, a new Location is being created. That way, the new posting will also be included in CampaignChain’s Call-to-Action tracking.
Finally, update the Activity module’s list of exposed services to include the new job. Remember that the name you assign to this job service must match the name specified for the job in the Activity module’s campaignchain.yml file.
To do this, update the file at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/services.yml so it now looks like the following.
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/services.yml
parameters:
services:
acme.operation.linkedin.job.share_news_item:
class: Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Job\ShareNewsItem
arguments: [ @doctrine.orm.entity_manager, @service_container ]
acme.operation.linkedin.news_item:
class: Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\EntityService\NewsItem
arguments: [ @doctrine.orm.entity_manager ]
7. Create Activity and Operation Routes¶
In general, an Activity module should specify the routes for creating and editing operations. This implies that the Activity module should define four routes:
- A route to create a new activity (‘new’)
- A route to edit an existing activity (‘edit’)
- A route to edit an existing activity in the campaign timeline’s pop-up/lightbox view (‘edit_modal’)
- A route for the submit action of the pop-up/lightbox view in the campaign timeline (‘edit_api’)
When defining the campaignchain.yml file for the Activity module, you specified names for all these routes. The next step is to connect those names with Symfony controllers and actions.
To do this, update the file your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml as shown below:
# src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml
acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_new:
pattern: /activity/linkedin/share-news-item/new
defaults: { _controller: AcmeCampaignChainActivityLinkedInBundle:ShareNewsItem:new }
acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_edit:
pattern: /activity/linkedin/share-news-item/{id}/edit
defaults: { _controller: AcmeCampaignChainActivityLinkedInBundle:ShareNewsItem:edit }
acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_edit_modal:
pattern: /modal/activity/linkedin/share-news-item/{id}/edit
defaults: { _controller: AcmeCampaignChainActivityLinkedInBundle:ShareNewsItem:editModal }
acme_campaignchain_activity_linkedin_share_news_item_edit_api:
pattern: /api/private/activity/linkedin/share-news-item/byactivity/{id}/edit
defaults: { _controller: AcmeCampaignChainActivityLinkedInBundle:ShareNewsItem:editApi }
options:
expose: true
Note
You can delete the default ‘hello’ route added by the Symfony bundle generator in the above file. Similarly, you can delete the default ‘hello’ route in the Operation module’s routing.xml file, which can be found at your-project/src/Acme/CampaignChain/Operation/LinkedInBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml.
8. Create an Activity Controller¶
Next, you’ll need to create views and controllers for the routes above. First up, you’ll handle the ‘new’ route, by creating a controller with a createAction() method, as shown below.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/Controller/ShareNewsItemController.php
namespace Acme\CampaignChain\Activity\LinkedInBundle\Controller;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Medium;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Session\Session;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Operation;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Form\Type\ShareNewsItemOperationType;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Serializer;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Encoder\JsonEncoder;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Normalizer\GetSetMethodNormalizer;
class ShareNewsItemController extends Controller
{
const BUNDLE_NAME = 'acme/activity-linkedin';
const MODULE_IDENTIFIER = 'acme-linkedin-share-news-item';
const OPERATION_IDENTIFIER = self::MODULE_IDENTIFIER;
public function newAction(Request $request)
{
$wizard = $this->get('campaignchain.core.activity.wizard');
$campaign = $wizard->getCampaign();
$activity = $wizard->getActivity();
$activity->setEqualsOperation(true);
$activityType = $this->get('campaignchain.core.form.type.activity');
$activityType->setBundleName(self::BUNDLE_NAME);
$activityType->setModuleIdentifier(self::MODULE_IDENTIFIER);
$shareNewsItemOperation = new ShareNewsItemOperationType(
$this->getDoctrine()->getManager(), $this->get('service_container'));
$operationForms[] = array(
'identifier' => self::OPERATION_IDENTIFIER,
'form' => $shareNewsItemOperation,
'label' => 'LinkedIn Message',
);
$activityType->setOperationForms($operationForms);
$activityType->setCampaign($campaign);
$form = $this->createForm($activityType, $activity);
$form->handleRequest($request);
if ($form->isValid()) {
$activity = $wizard->end();
// Get the operation module.
$operationService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.operation');
$operationModule = $operationService->getOperationModule(
'acme/operation-linkedin',
'acme-linkedin-share-news-item'
);
// The activity equals the operation.
// Thus, we create a new operation with the same data.
$operation = new Operation();
$operation->setName($activity->getName());
$operation->setActivity($activity);
$activity->addOperation($operation);
$operationModule->addOperation($operation);
$operation->setOperationModule($operationModule);
// The Operation creates a Location, i.e. the post
// will be accessible through a URL after publishing.
// Get the location module for the user stream.
$locationService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.location');
$locationModule = $locationService->getLocationModule(
'acme/location-linkedin',
'acme-linkedin-user'
);
$location = new Location();
$location->setLocationModule($locationModule);
$location->setParent($activity->getLocation());
$location->setName($activity->getName());
$location->setStatus(Medium::STATUS_UNPUBLISHED);
$location->setOperation($operation);
$operation->addLocation($location);
// Get the status data from request.
$status = $form->get(self::OPERATION_IDENTIFIER)->getData();
// Link the status with the operation.
$status->setOperation($operation);
$repository = $this->getDoctrine()->getManager();
// Make sure that data stays intact by using transactions.
try {
$repository->getConnection()->beginTransaction();
$repository->persist($activity);
$repository->persist($status);
// We need the activity ID for storing the hooks. Hence we must flush here.
$repository->flush();
$hookService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.hook');
$activity = $hookService->processHooks(self::BUNDLE_NAME,
self::MODULE_IDENTIFIER, $activity, $form, true);
$repository->flush();
$repository->getConnection()->commit();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$repository->getConnection()->rollback();
throw $e;
}
$this->get('session')->getFlashBag()->add(
'success',
'Your new LinkedIn activity <a href="'.
$this->generateUrl(
'campaignchain_core_activity_edit',
array('id' => $activity->getId())
).
'">'.$activity->getName().
'</a> was created successfully.'
);
if ($form->get('campaignchain_hook_campaignchain_due')->has('execution_choice')
&& $form->get('campaignchain_hook_campaignchain_due')
->get('execution_choice')->getData() == 'now') {
$job = $this->get('acme.operation.linkedin.job.share_news_item');
$job->execute($operation->getId());
}
return $this->redirect(
$this->generateUrl('campaignchain_core_activities')
);
}
return $this->render(
'CampaignChainCoreBundle:Base:new.html.twig',
array(
'page_title' => 'New LinkedIn News Item',
'page_secondary_title' => 'Campaign "'.$campaign->getName().'"',
'form' => $form->createView(),
));
}
}
The createAction() method begins by initializing CampaignChain’s Activity Wizard, which takes care of presenting the user with a form that lists available campaigns and activities. Based on the information received in the form, the Activity Wizard gets references to the correct Campaign and Activity. Since by design this Activity has only one Operation, the setEqualsOperation() method is used to tell CampaignChain that the Activity and the Operation are to be treated as the same entity.
The controller then initializes and renders the Form object created earlier using the createForm() method, so that the user can enter the necessary details for the Activity - in this case, the news item to be posted. If the form input is valid, the script creates a new Operation object with the same data as the Activity object. The Operation is then added to the Activity with the Activity object’s addOperation() method.
At the same time, once the Operation succeeds, a new Location will be created representing the news item on LinkedIn. Therefore, the controller invokes the Location service and defines basic data for the Location. This Location record is by necessity incomplete at this stage as the news item has yet to be published on LinkedIn; if you refer to the Job created earlier, you will see that the Job updates the Location record with the URL to the news item once it is executed.
Once all the relationships are established, the data is saved to the CampaignChain database and a success message is displayed to the user. The final execution of the operation is handled by the CampaignChain job scheduler at the appropriate time. The above code however demonstrates how the operation can be executed immediately if required, by invoking the Job service and calling the Job’s execute() method.
In a similar vein, you can handle the ‘edit’ route by defining an editAction() method, which takes care of editing an existing activity/operation.
<?php
// src/Acme/CampaignChain/Activity/LinkedInBundle/Controller/ShareNewsItemController.php
namespace CampaignChain\Activity\LinkedInBundle\Controller;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Location;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Medium;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Session\Session;
use CampaignChain\CoreBundle\Entity\Operation;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Acme\CampaignChain\Operation\LinkedInBundle\Form\Type\ShareNewsItemOperationType;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Serializer;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Encoder\JsonEncoder;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Normalizer\GetSetMethodNormalizer;
class ShareNewsItemController extends Controller
{
public function editAction(Request $request, $id)
{
$activityService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.activity');
$activity = $activityService->getActivity($id);
$campaign = $activity->getCampaign();
// Get the one operation.
$operation = $activityService->getOperation($id);
$operationService = $this->get('acme.operation.linkedin.news_item');
$newsitem = $operationService->getNewsItemByOperation($operation);
$activityType = $this->get('campaignchain.core.form.type.activity');
$activityType->setBundleName(self::BUNDLE_NAME);
$activityType->setModuleIdentifier(self::MODULE_IDENTIFIER);
$shareNewsItemOperation = new ShareNewsItemOperationType(
$this->getDoctrine()->getManager(), $this->get('service_container')
);
$shareNewsItemOperation->setNewsItem($newsitem);
$operationForms[] = array(
'identifier' => self::OPERATION_IDENTIFIER,
'form' => $shareNewsItemOperation,
'label' => 'LinkedIn Message',
);
$activityType->setOperationForms($operationForms);
$activityType->setCampaign($campaign);
$form = $this->createForm($activityType, $activity);
$form->handleRequest($request);
if ($form->isValid()) {
// Get the status data from request.
$status = $form->get(self::OPERATION_IDENTIFIER)->getData();
$repository = $this->getDoctrine()->getManager();
// The activity equals the operation.
// Thus, we update the operation with the same data.
$activityService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.activity');
$operation = $activityService->getOperation($id);
$operation->setName($activity->getName());
$repository->persist($operation);
$repository->persist($status);
$hookService = $this->get('campaignchain.core.hook');
$activity = $hookService->processHooks(
self::BUNDLE_NAME, self::MODULE_IDENTIFIER, $activity, $form
);
$repository->persist($activity);
$repository->flush();
$this->get('session')->getFlashBag()->add(
'success',
'Your LinkedIn activity <a href="'.
$this->generateUrl(
'campaignchain_core_activity_edit',
array('id' => $activity->getId())
).'">'.$activity->getName().
'</a> was edited successfully.'
);
if ($form->get('campaignchain_hook_campaignchain_due')->has('execution_choice')
&& $form->get('campaignchain_hook_campaignchain_due')
->get('execution_choice')->getData() == 'now') {
$job = $this->get('acme.operation.linkedin.job.share_news_item');
$job->execute($operation->getId());
}
return $this->redirect($this->generateUrl('campaignchain_core_activities'));
}
return $this->render(
'CampaignChainCoreBundle:Base:new.html.twig',
array(
'page_title' => 'Edit LinkedIn News Item',
'page_secondary_title' => 'Campaign "'.$campaign->getName().'"',
'form' => $form->createView(),
));
}
}
The editAction() action method is very similar to the createAction() method described previously, with the primary difference being that it uses the identifier passed in the URL string to retrieve a specific activity or operation and pre-populate the input form with the details of that activity or operation.
Note
The editModalAction() and editApiAction() method implement functionality similar to that of the editAction() method. They are not included here but can be viewed in the source code of the corresponding LinkedIn bundle on Github.
It’s important to note that all the action methods described above use CampaignChain’s base views, and it is not necessary to create new views unless you specifically wish to override the base views.
At this point, your Activity and Operation bundles are complete. Once you add your modules to CampaignChain through the module installer, you should be able to connect to a new LinkedIn location and begin posting news items to it.